| NIES-MCC | KU-MACC | Tree to Strain | Japanese | English |
| Life / Eukarya / Plantae / Viridiplantae / Chlorophyta / Chlorophyceae | |
|
Oedogoniales(Oedogonium, Bulbochaete etc.) Chaetopeltidales(Chaetopeltis, Hormotillopsis etc.) Chaetophorales(Chaetophora, Stigeoclonium, Uronema etc.) Sphaeropleales(Scenedesmus, Pediastrum, Ankistrodesmus etc.) Volvocales(Chlamydomonas, Volvox, Chlorococcum etc.) |
| Referece |
|
|
The Chlorophyceae includes many familiar phytoplanktonic green algae such as Chlamydomonas, Scenedesmus and Pediastrum. Most chlorophycean algae are photosynthetic, but colorless heterotrophic species are also known (Polytoma, Polytomella etc.). The chlorophycean algae are abundant in freshwater, but the members of the Volvocales include many marine species. Chlamydomonas is a common model organism for biology. Chlorophycean algae are unicellular, colonial or filamentous. Most species are non-motile, but many species of the Volvocales are flagellate. Cells are naked or covered by cellulosic or glycoprotein cell wall. Cytokinesis is mediated by phycoplast. In the Chaetophorales and Oedogoniales, the cell plates are also associated in the cytokinesis to form plasmodesmatae. The flagellate cell usually possesses rotationally symmetrical cell architecture and two or four flagella inserted apically. The opposed basal bodies are directly opposed or displaced clockwise. Asexual reproduction is caused by binary fission, zoosporogenesis, sporogenesis etc. Sexual reproductions by isogamy, anisogamy or oogamy are known. Most species with sexual reproduction show haplontic life cycle, in which the zygote is only diploid stage. Isomorphic alternation of generation is reported in some members of the Chaetophorales, but some phycologists doubt. |
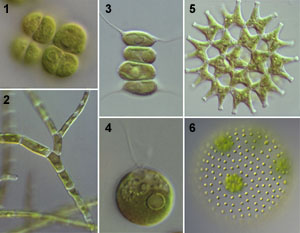 1: Desmotetra (Volvocales, NIES-153). 2: Stigeoclonium (Chaetophorales, NIES-532). 3: Desmodesmus (Sphaeropleales, NIES-96).4: Chlamydomonas (Volvocales, NIES-437). 5: Pediastrum (Sphaeropleales, NIES-211). 6: Volvox (Volvocales, NIES-541). |