| NIES-MCC | KU-MACC | Tree to Strain | Japanese | English |
| Life / Eukarya / Plantae / Viridiplantae / Chlorophyta / Chlorophyceae / Chaetophorales | |
|
Schizomeris Aphanochaete Uronema (NIES-538, 539, 540) Fritschiella Chaetophora Stigeoclonium (NIES-531, 532) Draparnaldia Cloniophora |
| References |
|
|
Filamentous green algae inhabiting in freshwater. Some species such as Fritschiella live on soil. The chloroplast genome sequemce is reported for Stigeoclonium helveticum (Bélanger et al. 2006, Molecular Genetics and Genomics 276: 464-477). The chaetophoralean algae show branched or unbranched filamentous organization. Some species form foliose thalli. The holdfast cell is usually differenciated. Plasmodesmatae are present. Each cell is uninucleate and possesses a paraietal chloroplast with pyrenoid traversed by thylakoids. Cytokinesis involves phycolast and cell plates. The flagellate cell is naked, possesses two or four flagella inserted apically. In the quadriflagellate cells, four basal bodies are arranged in upper and lower pairs. The upper basal bodies are directly opposed, and the lower basal bodies are displaced clockwise. Asexual reproduction by means of zoospore, aplanospore, akinete or fragmentation. The zoospores are usually quadriflagellate, but biflagellate zoospores are also known. Isogamy by biflagellate gametes is reported. Isomorphic alternation of generation (gametophyte and sporophyte) is reported for some species, but some phycologists doubt. |
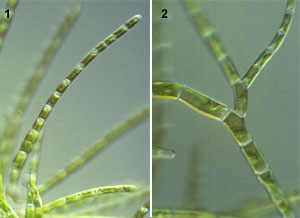 1: Uronema (NIES-540). 2: Stigeoclonium (NIES-532). |