| NIES-MCC | KU-MACC | Tree to Strain | Japanese | English |
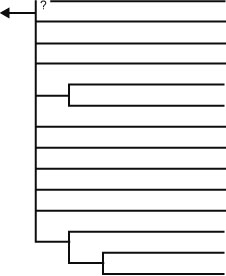
| Life / Eukarya / Plantae / Viridiplantae / Chlorophyta / Chlorophyceae / Sphaeropleales | |
|
Mychonastes homosphaera / Korshpalmella / Pseudodictyosphaerium "Muriella" zofingiensis (= "Chlorella" zofingiensis, "Mychonastes" zofingiensis) Pseudomuriella (= Muriella aurantiaca) Sphaeropleaceae (Ankyra, Atractomorpha, Sphaeroplea etc.) Pseudoschroederia Schroederia Schizochlamys Planktosphaeria Dictyochloris Bracteacoccus Selenastraceae (Monoraphidium, Ankistrodesmus, Pseudokirchneriella etc.) Scenedesmaceae (Scenedesmus, Desmodesmus, Coelastrum, Dimorphococcus etc.) Neochloridaceae (Polyedriopsis, Neochloris, Characiopodium etc.) Hydrodictyaceae (Pediastrum, Hydrodictyon, Chlorotetraedron) |
| References |
|
|
The Sphaeropleales includes common freshwater phytoplanktons such as Scenedesmus, Desmodesmus, Pediastrum. The sphaeroplealean algae are unicellular, colonial or unbranched filamentous. There are many coenobial species such as Scenedesmus and Pediastrum. Hydrodictyon forms macroscopic coenobium. The cell wall is cellulosic, and usually covered by outermost trilaminar layer composed of sporopollenin-like material. The young vegetative cell is uninucleate, but matured cell is usually multinuclear. The flagellate cell is naked and possesses two flagella inserted apically. Basal bodies are directly opposed. Cytokinesis involves phycoplast and furrowing. Asexual reproduction is caused by formation of zoospores, autospores or daughtercolonies. Sexual reproductions by isogamy or oogamy are known. |
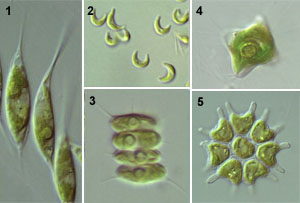 1: Schroederia (NIES-246). 2: Monoraphidium (Selenastraceae, NIES-480). 3: Desmodesmus (Scenedesmaceae, NIES-798). 4: Polyedriopsis (Neochloridaceae, NIES-232). 5: Pediastrum (Hydrodictyaceae, NIES-301). |