| NIES-MCC | KU-MACC | Tree to Strain | Japanese | English |
| Life / Eukarya / Plantae / Viridiplantae / Chlorophyta / Trebouxiophyceae | |
|
Chlorellales (Chlorella, Micractinium, Picochlorum, Auxenochlorella etc.) Oocystaceae (Oocystis, Lagerheimia, Eremosphaera etc.) Microthamniales (Microthamnion, Fusochloris etc.) Choricystis-clade (Choricystis, Botryococcus, Coccomyxa etc.) Trebouxiales (Trebouxia, Pseudotrebouxia, Myrmecia, Diplosphaera, Asterochloris (?) etc.) Prasiolales (Prasiola, Stichococcus, Raphidonema, "Chlorella" ellipsoidea etc.) Watanabea-clade (Watanabea, Dictyochloropsis, "Chlorella" saccharophila etc.) Lobosphaera Leptosira Parietochloris Coenocystis Others |
| Reference |
|
|
Unicellular to macroscopic green algae. Most species live in freshwater or on land, but marine species are also present. Some trebouxiophycean algae (e.g. Trebouxia) are phycobionts of lichens. Chlorella is a famous trebouxiohycean algae sometimes used for healthy foods, but the generic name has been applied to various green algae (some chlorophycean species were classified in the genus). Some heterotrophic colorless trebouxiophycean algae such as Prototheca and Helicosporidium are parasitic on human and domestic animals. Most species are unicellular, but colonial and filamentous species are also known. Some species of Prasiola form macroscopic thalli. The flagellate cell possesses two homodynamic equal flagella inserted apically. The basal bodies are displaced counterclockwise. Cytokinesis is mediated by phycoplast. Centrioles (if present) are located near the equator (metacentric spindle). Asexual reproduction is caused by binary fission, budding, zoosporogenesis, sporogenesis, etc. The reports on the sexual reproduction of the Trebouxiophyceae are rare, but oogamy is known for some species. |
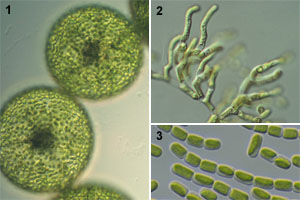 1: Eremosphaera (NIES-644). 2: Microthamnion (NIES-479). 3: Stichococcus (NIES-530). |